Quantitative tightening is a monetary policy tool used by central banks (like the FED) to tighten the money supply. This is done by selling government bonds and other securities in the open market.
The goal of quantitative tightening is to reduce the money supply and make it harder for people and businesses to borrow money. This can help cool down an overheated economy and prevent inflation.
QT Vs. QE Video Comparison and Explanation
Follow us on YouTube to see more videos like this: » Subscribe Now!
What Is Quantitative Tightening (QT)?
Quantitative tightening is the process of the Federal Reserve (FED) sells its securities in the open market in order to reduce the money supply. The Fed believes that this will help to moderate inflation and keep the economy stable.
Earlier Start of Quantitative Tightening (QT)
The process began in October 2017, when the Fed announced that it would begin to shrink its balance sheet by reducing its reinvestment of principal payments from its securities holdings. After the beginning of the cycle containing the first price increase, which took place in December 2015, the cycle experienced two years.
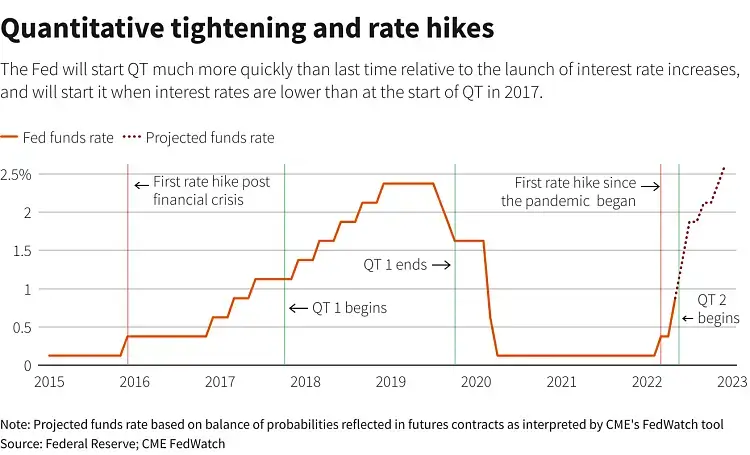
In a statement released after its two-day policy meeting, the Fed said it will reduce its holdings of Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities by $10 billion starting in October. The move reflects the central bank’s confidence in the economy as it enters its ninth year of expansion.
The Fed also signaled that it plans to raise interest rates another time this year and three times next year, faster than previously expected. That would bring the benchmark federal funds rate to 3.1 percent by the end of 2019, up from 1.9 percent currently.
How QT does it work?
As we said before, the Federal Reserve (FED) is in the process of quantitative tightening (QT) when it is selling its holdings of bonds and other securities back into the market.
- The goal is to reduce the size of its balance sheet and tighten monetary policy.
- Bond prices fall when the Fed sells bonds, and this can lead to a rise in interest rates.
So far, the impact of QT has been limited. But it could become more important if inflation starts to pick up. Learn more about inflation and hyperinflation effects in the economy.
The Benefits of Quantitative Tightening
- The benefits of QT include a stronger dollar and lower inflation.
A stronger dollar makes U.S. exports more competitive, while lower inflation gives the Fed more room to cut interest rates if needed
The Risks of Quantitative Tightening
- Critics of QT argue that it could cause a recession.
However, the Fed has signaled that it will continue to use QT until it achieves its goals.
In conclusion, quantitative tightening is the process of the Federal Reserve shrinking its balance sheet. This can have a variety of impacts on the economy, including higher interest rates and a stronger dollar. It’s important to keep an eye on how the Fed’s actions will affect you and your investments.
